X
X - Products
- Solutions
- Support
- Contact
- Order Online

 X
X - BACK
- Power Meters
- Control Panels
- Current Transformers
- BAS Sensors
- Communication Devices
- Energy Software
- Applications
- Resource Center
 X
X - BACK
- All Power Meters
- Acuvim 3Power Quality Meter & Analyzer
- Acuvim II SeriesAdvanced Multifunction Power Meters
- Acuvim IIBNBACnet Power & Energy Meter
- Acuvim L SeriesMultifunction Energy Meters
- EV300 SeriesPower & Energy Panel Meters
- AcuRev 2100 SeriesMulti-Circuit Submeters
- AcuRev 2000 SeriesMulti-Channel Submeters
- AcuRev 1310 SeriesDIN-Rail 3-Phase Energy Meters
- AcuDC 300 SeriesEV Charging Meter
- AcuDC 240 SeriesDC Power & Energy Meters
- Tesla Power MetersTesla Power Meter Order Form
- All Communication Devices
- AcuHMIHMI & Gateway
- AcuLink 810DAQ Gateway & Server
- AcuMeshWireless Modbus-RTU Transceiver
- AXM-WEB2WiFi, Dual Ethernet Module
- AXM-WEB2 FOLCFiber Optics, WiFi, Ethernet Module
- AXM-WEB2-DDual Ethernet Module
- AcuDC 240 ModulesComm. Expansion for AcuDC 240 Meters
- All Pre-Wired Control Panels
- AcuPanel 9108X SeriesPre-Wired Control Panel for Acuvim 3 Power Quality Meter
- AcuPanel 9104XAcuPanel 9104X Pre-Wired Power Metering Control Panel
- AcuPanel 9106XAcuPanel 9106X Pre-Wired Multi-Channel Submetering Control Panel
- AcuPanel 9104X-DCAcuPanel 9104X-DC Pre-Wired DC Metering Control Panel
- UL 508A Panel ShopPre-Wired Custom Contol Panel
- AcuCloud Login
- AcuCloud EMSCloud-based Energy Management Solution
- Metering Data Collection
- Tenant Billing Software
- Energy Analysis & Reporting
- Utility Billing Software
- All Application Solutions
- DC Metering
- Energy Efficiency
- Metering
- Panel Metering
- Power Distribution
- Power Quality
 X
X - BACK
- All Rogowski Coils
- AcuCT Flex SeriesFlexible Current Transformers
- RIK 1AR Flexible CTProtection Relay 1A Output
- RIK 5A Flexible CT5A Output Integrator
- RIK 333mV Flexible CT333mV Output Integrator
- RIK 4-20mA / 0-20mA CT4-20mA or 0-20mA Output Integrator
- RIK 0-5V / 0-10V CT0-5V or 0-10V Output Integrator
- All Split-Core CTs
- AcuCT R SeriesRevenue-Grade Split-Core CT
- AcuCT 5A Series5A Split-Core Current Transformers
- AcuCT mV Series333mV Split-Core CT
- AcuCT Hinged SeriesBranch Circuit 333mV CT
- All Solid-Core CTs
- AcuCT S77Revenue-Grade Solid-Core CT
- AcuCT S1135A Solid-Core Current Sensor
- AcuCT S125Solid-Core CT
- AcuCT S165Solid-Core CT
- AcuCT S220Switchgear Solid-Core CT
- AcuCT S335Busbar Solid-Core CT
- AcuCT S433Instrument Solid-Core CT
- AcuCT S650Solid-Core CT
- All DC Sensors
- HAB 16555DC Current Sensors
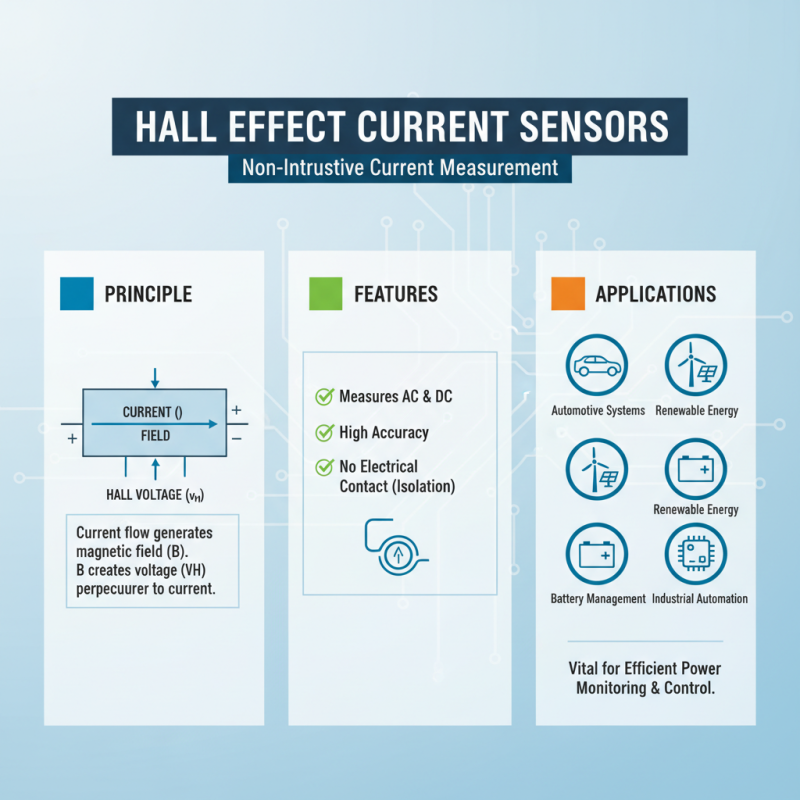
- HAK SeriesHall Effect Current Sensors
- DC Shunts0.1 - 0.5% Accuracy
- HV2DC High Voltage Sensor
- All CT Accessories
- RCT GRIP KitRogowski Mount Installation Kit
- AcuCT C5A to 80mA/100mA CT Converter
- All Differential Pressure Sensors
- AcuPRE DMDuct Mount Differential Pressure Sensor
- AcuPRE PMPanel Mount Differential Pressure Sensor
- AcuPRE WMWall Mount Differential Pressure Sensor
- All RH & Temperature Sensors
- AcuHUM DMDuct Mount RH Sensor
- AcuHUM RMRoom Mount RH Sensor
- AcuHUM OA/OAWOutdoor Air RH Sensor
- All Temperature Sensors
- AcuTEMS DMDuct Mount Temperature Sensors
- AcuTEMS IMImmersion Temperature Sensors
- AcuTEMS OAOutside Air Temperature Sensors
- AcuTEMS RMRoom Mount Temperature Sensors
- AcuTEMS WP304SS Wall Plate Temperature Sensors
- All DC Metering
- DC Circuit MonitoringDC Metering for Renewable Systems
- EV Charging StationsEnergy Metering for EV
- All Energy Efficiency
- Energy AuditsMetering Energy Audits
- Time-of-Use MeteringUnderstanding Peaks, Off-Peak Periods
- All Metering
- Tenant SubmeteringHow Tenant Submetering Works
- Branch Circuit MonitoringDense Circuit Metering Implementation
- HVAC MeteringHVAC Energy Management
- Remote MeteringRemote Metering and Monitoring
- kWh MeteringWhat is Kilowatt-Hour Metering